3.3. Basic shell commands
Unix shell
From Wikipedia:
Unix shell is a command-line interpreter [...] that provides a command line user interface for Unix-like operating systems. The shell is both an interactive command language and a scripting language, and is used by the operating system to control the execution of the system using shell scripts.
Users typically interact with a Unix shell using a terminal emulator;
If that does not mean much to you, this is what a terminal and shell commands look like:
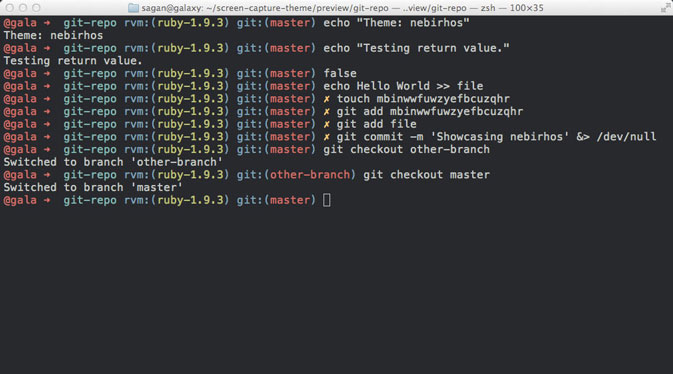
Figure from Oh My Zsh.
Some basic Unix shell commands
Change the working directory.
cd ~/tmpList the contents of the working directory.
$ lsCreate an empty file.
$ touch file.txtCreate a copy of the file.
$ cp file.txt copy-of-file.txtMove the file (and/or rename it).
$ mv file.txt file2.txtCreate a new folder.
$ mkdir tmpDelete a file.
$ rm file.txtDelete a directory.
$ rm -r ~/tmpWrite to a file overwriting its contents.
$ echo Hello world > file.txtWrite to a file by appending to its contents.
$ echo Hello again world >> file.txtPrint the contents of the file on the terminal.
$ cat file.txtDisplay the contents of the file on the terminal page-by-page.
$ less file.txtIf you are using windows...
On Windows, many of these commands are different.
Check the table below for a list of Windows equivalent commands.
| Windows | Linux | Description |
|---|---|---|
dir |
ls -l |
List the contents of the current directory. |
copy |
cp |
Copy a file. |
ren |
mv |
Rename a file. |
move |
mv |
Move a file. |
cls |
clear |
Clear the screen. |
del |
rm |
Delete files. |
fc |
diff |
Compare contents of files. |
find |
grep |
Search for a string in a file. |
cd |
cd |
Change the current directory. |
chdir |
pwd |
Return your current directory location. |
md |
mkdir |
Create a new directory/folder. |
echo |
echo |
Print something on the screen. |
edit |
vim (depends on editor) |
Write into file. |
exit |
exit |
Leave the terminal/command window. |
rmdir |
rm -rf / rmdir |
Delete a directory. |
tree |
ls -R |
List a directory recursively. |
type |
cat |
Print the contents of a file. |
This table was adapted from this source.
Windows Subsystem for Linux
Alternatively, Windows users can install the Windows Subsystem for Linux.
Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL) lets developers run a GNU/Linux environment -- including most command-line tools, utilities, and applications -- directly on Windows, unmodified, without the overhead of a traditional virtual machine or dual-boot setup.